Parameter Group Numbers (PGNs) are a fundamental component of the SAE J1939 protocol, a vehicle network protocol used for communication and diagnostics in heavy-duty vehicles. PGN categorize and standardize messages exchanged between ECUs, ensuring reliable and efficient data transmission. They help identify the type and purpose of each message, such as engine speed, fuel economy, or diagnostic data. By understanding PGNs, engineers can decode CAN messages accurately and design systems that interact seamlessly within the J1939 network. Let’s discuss PGNs in detail.
Table of Contents
Structure of a PGN in SAE J1939
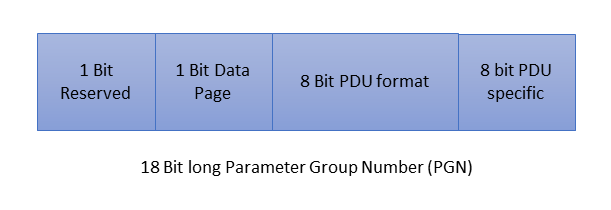
A PGN is a 18-bit identifier that categorizes messages within the SAE J1939 protocol. It is part of the 29-bit CAN Identifier. The structure of a PGN is as follows:
- Reserved (1 bit): This bit is reserved for future use.
- Data Page (1 bit): Indicates the Data Page of the message.
- PDU Format (8 bits): Specifies the format of the Protocol Data Unit (PDU).
- PDU Specific (8 bits): Further categorizes the PDU format.
This structure allows for a large number of unique PGNs, each representing a specific type of data or message. And, here is the PGN representation inside a 29-bit CAN message:
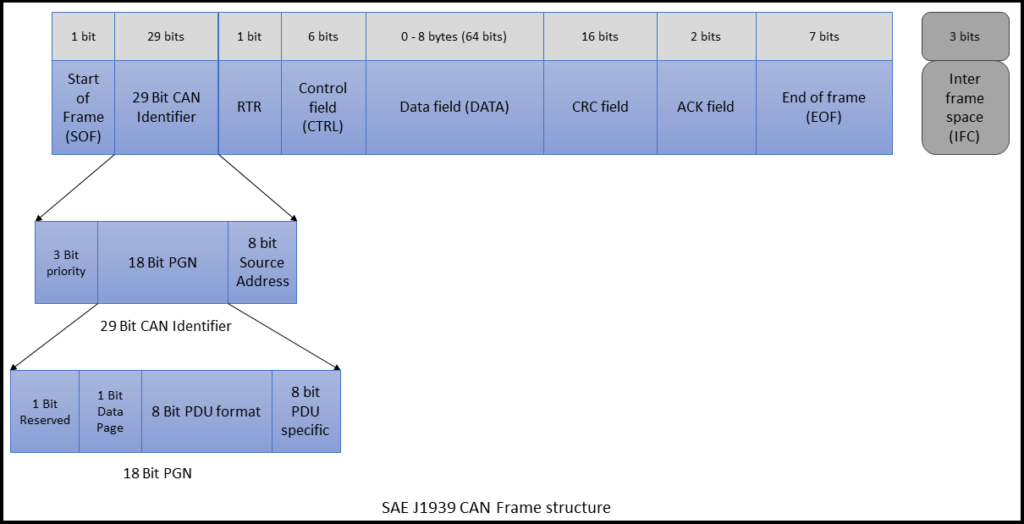
Detailed overview of content of a PGN
Each PGN consists of specific fields such as priority, data page, PDU format, PDU specific and source address, which together define the message structure and routing. Understanding these fields allows developers to extract meaningful information from raw CAN frames and enables precise communication between different ECUs on the network. Now, lets discuss the content of a PGN in detail and understand how to interpret it.
PGN 59904 (0x00EA00)
GN 59904 request a Parameter Group from a single device or all devices in the network.
0x00EA00 (i.e. ‘00’ + ‘EA’ + ‘00’ -> 3 bytes)
Data Page = 0, Default Priority = 6
Data Description = Byte 1, 2, 3 = Requested Parameter Group Number
PDU Format = 234 (EA), PDU Specific = Destination Address (Global or Specific)
PGN 59392 (0x00E800)
PGN 59392 provides handshake between transmitting and responding nodes.
Data Page = 0, Default Priority = 6
PDU Format = 232 (EB), PDU Specific = Destination Address (Global = 255)
Data Description = Byte 1….8 = Positive Ack, Negative Ack, Access Denied or cannot respond.
PGN 60416 (0x00EC00)
PGN 60416 is used for communication management flow-control (example BAM).
Data Page = 0, Default Priority = 7
PDU Format = 236 (EC), PDU Specific = Destination Address (= 255 for broadcast)
Data Description = (for BAM Only)
Byte 1 = Control Byte = 32
Byte 2 – 3 = Message Size (number of bytes)
Byte 4 = Total number of packages
Byte 5 = Reserved (should be filled with FF hex)
Byte 6 – 8 = PGN of multi-packet message (6 = L.S.B. and 8 = M.S.B.)
PGN 60160 (0x00EB00)
PGN 60160 is used for data transfer of multi-packet messages.
Data Page = 0, Default Priority = 7
PDU Format = 235 (EB), PDU Specific = Destination Address
Data Description:
Byte 1 = Sequence number (1 to 255)
Byte 2 – 8 = Data
Types of PGN
PGNs can be categorized into two main types based on their PDU format:
- Point-to-Point (PDU1 Format): Used for messages that are addressed to a specific ECU. The destination address is included in the message.
- Broadcast (PDU2 Format): Used for messages that are broadcast to all ECUs on the network. These messages do not include a specific destination address.
Commonly Used PGN in SAE J1939
PGNs are essential identifiers in the SAE J1939 protocol, used to define the type of data being transmitted between electronic control units. Understanding commonly used PGNs helps engineers interpret vehicle messages accurately and ensures effective communication across the network.
Diagnostic Messages in SAE J1939
Diagnostic messages are crucial for monitoring and troubleshooting vehicle systems. Some commonly used diagnostic PGNs include:
- PGN 65226 (DM1 – Active Diagnostic Trouble Codes): Transmits active diagnostic trouble codes from the ECUs.
- PGN 65227 (DM2 – Previously Active Diagnostic Trouble Codes): Reports previously active diagnostic trouble codes.
- PGN 65228 (DM3 – Diagnostic Data Clear/Reset): Requests clearing or resetting of diagnostic data.
Vehicle System Messages in SAE J1939
Vehicle system messages convey information about various subsystems within the vehicle. Key PGNs in this category include:
- PGN 61443 (Electronic Engine Controller 1 – EEC1): Provides engine speed, torque, and status information.
- PGN 65265 (Electronic Transmission Controller 1 – ETC1): Contains transmission-related data such as gear position and shift status.
- PGN 65300 (Fuel System): Delivers data about fuel levels, consumption, and pressure.
Engine Messages in SAE J1939
Engine messages are vital for engine control and monitoring. Some important engine-related PGNs are:
- PGN 65247 (Electronic Engine Controller 2 – EEC2): Reports engine temperature, pressure, and other critical parameters.
- PGN 65253 (Engine Fluid Level/Temperature): Provides information on engine fluid levels and temperatures.
- PGN 65263 (Turbocharger Information): Transmits data about turbocharger performance and status.
Final Thoughts
PGNs play a crucial role in the SAE J1939 protocol by ensuring that data is accurately categorized and easily identifiable. By using predefined PGNs, manufacturers and service technicians can quickly interpret data and diagnose issues.
Understanding the different Parameter Group Numbers in the SAE J1939 protocol is essential for anyone involved in the design, maintenance, and operation of heavy-duty vehicle, tractors, earth moving vehicle networks. Also, on TractorManualPDF you can download and read a lot of Tractor Manuals, Spare Parts Catalogs, DTC lists and Electric Wiring Diagrams.
So to diagnose heavy duty vehicle, familiarizing yourself with common PGNs & their functions is important. With this information, you can enhance your ability to troubleshoot and optimize vehicle systems.