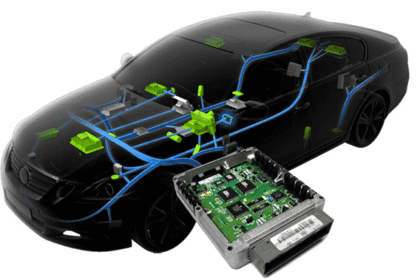
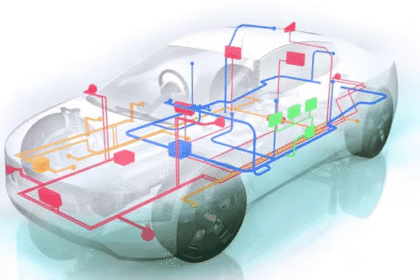
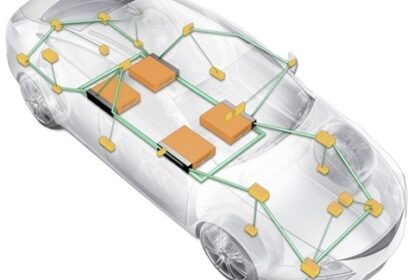
Software Defined Vehicles (SDV) represent a fundamental shift in automotive design where software and centralized compute define vehicle capability more than hardware modules. Functional Safety in SDV...
The concept of software defined vehicles (SDV) is a fundamental change in the engineering of vehicles, in which software happens to dominate the vehicle functionality as opposed to hardware. These veh...
India is rapidly building testing capacity for the electrification of mobility and its supporting electrical ecosystem. The Central Power Research Institute (CPRI) has inaugurated a regional testing l...
Cold climates present one of the toughest challenges for electric vehicles. When the thermometer dips below −30 °C, batteries suffer from high internal resistance, sluggish ion transport and significa...
Validating ECUs is vital for vehicle performance, safety and compliance. ECU validation ensures that communication between the control unit and diagnostic tools is accurate, secure and aligned with sp...
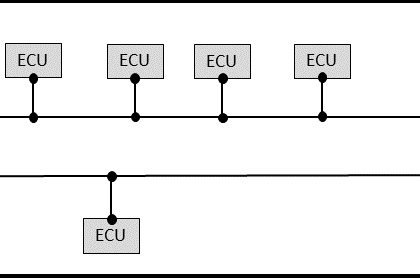
In modern vehicles and embedded systems, the CAN BUS and LIN protocol serve crucial but distinct roles. This article offers a deep technical comparison of CAN vs LIN, covering architecture, data rates...
MBUX stands for Mercedes Benz User Experience, an AI driven multimedia and infotainment system introduced in 2018 on the Mercedes A Class. It features dual TFT displays (instrument and infotainment), ...
CAN uses many ways to detect errors on the bus. There are majorly five error detection techniques in CAN bus protocol. These include Bit Monitoring, Bit Stuffing, Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC), Frame ...
The automotive industry is undergoing a major transformation, moving beyond traditional mechanical and hardware centric designs toward vehicles where software is the core driver of innovation and func...
End-of-Line testing is a critical phase in automotive manufacturing, ensuring that each ECU functions correctly before being integrated into vehicles. Given that modern vehicles can contain over 100 E...
The Diagnostic Communication Manager module in AUTOSAR plays a vital role in enabling standardized diagnostic communication between external tools and vehicle ECUs. A wide range of use cases of DCM mo...
On July 1, 2024, Vector Informatik GmbH, completed the full acquisition of CSM GmbH, a leading manufacturer of measurement technology based in Filderstadt, Germany. This strategic move solidifies a pa...
The Diagnostics over Internet Protocol (DoIP) is a standardized communication protocol (ISO 13400) for performing vehicle diagnostics and software updates over Ethernet. It enables faster and mor...
The CAN Transport Protocol (CAN-TP) physical layer defines the hardware & electrical characteristics of the CAN protocol and specifies how data is transmitted over the physical medium. It includes...
Parameter Group Numbers (PGNs) are a fundamental component of the SAE J1939 protocol, a vehicle network protocol used for communication and diagnostics in heavy-duty vehicles. PGN categorize and stand...
A CAN controller manages communication over the CAN bus. It handles tasks such as message framing, error detection & message arbitration to ensure reliable data exchange between ECUs. CAN Controll...
SAE J1939 communication is a in-vehicle networking protocol for ensuring seamless interaction between ECUs in heavy-duty vehicles. Understanding the different types of SAE J1939 communication is cruci...
Vehicle Spy (VSpy) is an automotive network analysis engineering tool that is widely used for monitoring, diagnosing, and simulating in-vehicle protocols such as CAN, LIN, CAN-FD, Automotive Ethernet ...
Each CAN message in a CAN protocol has a unique hexadecimal Identifier called as CAN-ID or CAN Arbitration ID. A CAN-ID uniquely identifies a CAN message. Specifically, there are two types of frames o...
In this article, we will first discuss the Diagnostic SID range, the UDS services list, and the different diagnostic protocols (UDS, SAE J1979 OBD-II) associated with them. Next, we will explain how e...
In the CAN protocol, USDT and UUDT diagnostic responses define a method for transmitting diagnostic data by dividing large amounts of information into smaller segments or frames. Understanding the dif...
What is Physical Addressing Vs Functional Addressing in CAN protocol? How do these two addressing schemes differ from each other? Physical addressing targets a specific ECU by using a unique address, ...
Reverse engineering a vehicle is a process of interpreting the meaning of message data without the aid of the database files or design documents. It involves a deep understanding of ECUs, in-vehicle n...