Adaptive AUTOSAR is a standardized software platform designed for high performance vehicle computing units and advanced automotive functions such as automated driving connectivity and data intensive services. The Adaptive Platform defines a runtime environment, a set of platform services and well-defined application interfaces so that independently developed software can be deployed, updated and integrated on high performance ECUs.
Vehicles now run complex functions that require more computing power flexible deployment and runtime adaptability. Classic AUTOSAR was designed for deeply embedded ECUs with strong real time constraints and static configuration. Adaptive AUTOSAR was introduced to address a different set of requirements centered on dynamic service-oriented applications running on POSIX like operating systems using modern C++ toolchains and middleware. The Adaptive Platform allows runtime installation and update of applications and supports rich communication patterns suitable for connectivity and autonomy.
Founding companies of the AUTOSAR partnership include BMW Robert Bosch Continental Mercedes Benz and Volkswagen. These companies and others steered the early evolution of the standard. AUTOSAR membership is large with over 350 partners worldwide reported by AUTOSAR. Many of the technical working groups are led by senior engineers from OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers who contribute domain specific expertise such as safety architecture or high-performance Ethernet design. Their collaboration ensures that the platform remains aligned with both industry needs and emerging automotive technologies like centralized compute and automated driving stacks.
Table of Contents
Core concepts and architecture of Adaptive AUTOSAR
Adaptive AUTOSAR is organized around three conceptual layers. Adaptive Applications often abbreviated as AA are user level programs typically written in modern C++ and packaged as Linux style executables. AUTOSAR Runtime for Adaptive applications abbreviated as ARA is the set of standardized APIs through which Adaptive Applications access platform services. Adaptive Platform foundation and services is the set of platform services such as service discovery persistence execution management communication management and security features that are provided to AAs via ARA.
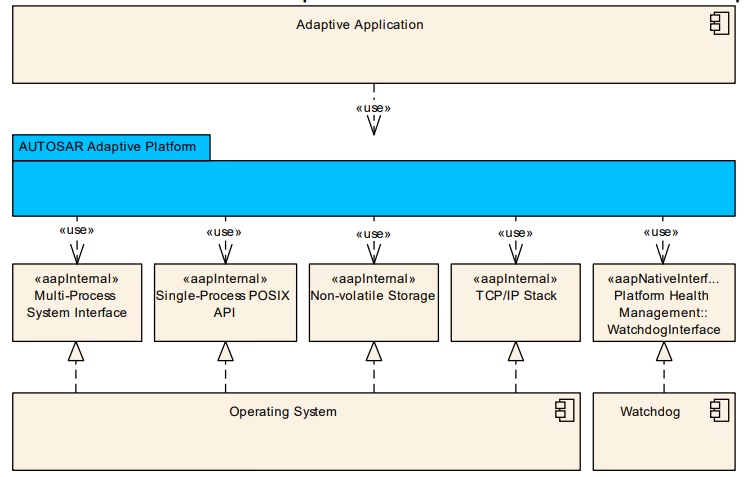
The Adaptive Platform specification groups functionality into functional clusters. Execution management controls application lifecycle and resource isolation. Communication management provides a service-oriented middleware supporting SOME IP and service discovery. Security and persistency services cover certificates keys and data storage. These elements are described in AUTOSAR explanatory architecture documents and the specification set. In practical terms this layered approach allows an adaptive application for autonomous driving to run alongside an infotainment control module on the same high-performance ECU without code interference as each uses standardized ARA calls.
The functional cluster separation ensures that communication management can be updated to support higher bandwidth Ethernet links without requiring changes to unrelated services like data persistency. From a performance standpoint the architecture enables efficient inter process communication through service-oriented patterns which can handle thousands of messages per second with deterministic latency when configured correctly.
The modular design also simplifies compliance testing as each functional cluster can be validated independently against AUTOSAR specifications. For example, a supplier developing a vehicle to cloud telemetry service can integrate it by implementing only the required communication and security APIs from ARA rather than rewriting low level operating system code.
AUTOSAR Runtime for Adaptive applications (ARA)
AUTOSAR Runtime for Adaptive applications (ARA) is the standardized interface set that Adaptive Applications use to access platform services. ARA includes APIs for service-based communication service discovery lifecycle management and persistency. The goal is API stability so that applications from different suppliers interoperate on a compliant platform.
This stability is critical because it allows a navigation application developed by one supplier to interact seamlessly with a vehicle to cloud connectivity service from another supplier without requiring proprietary integration work. ARA’s service discovery APIs, for example, enable an application to dynamically locate and bind to a required service at runtime, which is essential in adaptive systems where services may be updated or redeployed without stopping the entire platform.
In practical deployments ARA communication APIs often leverage SOME IP to enable high throughput and low latency exchange of structured data, making it suitable for tasks such as real time camera feed streaming or cooperative perception between vehicles. The lifecycle management aspect of ARA allows applications to be started, stopped or restarted under platform control, which is especially valuable in over the air update scenarios where certain components can be upgraded without affecting unrelated functions.
Persistency APIs within ARA ensure that critical data such as calibration parameters, user preferences or machine learning model weights are stored reliably in non-volatile memory, enabling consistent behavior across ECU reboots. This modularity and interoperability, when combined with a POSIX compliant operating system, enables automotive engineers to adopt modern software development practices such as continuous integration and automated testing while still meeting automotive safety and reliability standards.
Execution management
Execution management handles starting stopping monitoring and restarting of Adaptive Applications. It coordinates application deployment session control and health monitoring. This enables controlled updates and graceful degradation in the field. In practice execution management uses a predefined execution manifest that specifies the application’s startup parameters dependencies and required resources, ensuring that only compatible software components are launched on a given ECU.
For example, in an autonomous driving domain controller, execution management can delay the start of non-critical infotainment services until safety critical perception and control modules have fully initialized, thereby prioritizing system stability. When integrated with over the air update systems, execution management supports rolling updates where one application instance is replaced while others continue running, reducing downtime and avoiding full system reboots.
Furthermore, it provides isolation between applications so that a malfunction in one adaptive service, such as a corrupted navigation data parser, does not propagate to unrelated applications like driver monitoring or vehicle to cloud communication.
Communication management
Adaptive AUTOSAR uses a service-oriented approach. SOME IP is the most common service protocol used for in vehicle service-oriented communication. Service discovery and remote procedure semantics are core to how Adaptive Applications interact. The platform can also bridge to existing in vehicle networks. In a practical deployment a perception module can expose a lane detection service via SOME IP, which is then consumed by an automated steering application without requiring static binding at design time.
This flexibility allows engineers to integrate new high bandwidth Ethernet based services alongside legacy CAN or FlexRay networks by using gateway applications that translate between protocols while maintaining standardized ARA communication interfaces.
Security and safety
Adaptive AUTOSAR defines security interfaces for authentication authorization and secure storage. While functional safety is still an overall system responsibility the platform provides mechanisms to help meet safety requirements in mixed criticality environments. AUTOSAR publishes detailed specs and recommended practices for timing analysis and other safety related activities.
For instance, an adaptive application managing vehicle to cloud communication can use the security APIs to store cryptographic keys in a protected environment and enforce TLS based communication channels, ensuring both data integrity and confidentiality. In safety critical domains such as automated braking, the timing analysis recommendations help verify that latency from sensor input to actuator command remains within defined limits even when multiple adaptive services are sharing processing resources.
Adaptive AUTOSAR vs Classic AUTOSAR
| Topic | Classic AUTOSAR | Adaptive AUTOSAR |
| Primary use case | Low level embedded ECUs with strict real time | High performance ECUs running complex services |
| Programming language | C | C++ |
| Operating system | Bare metal or RTOS | POSIX style operating system such as Linux |
| Communication model | Signal oriented and static ports | Service oriented dynamic discovery |
| Deployment model | Static one-time flashing | Runtime installation update and lifecycle management |
| Real time focus | Hard real time | Soft real time or best effort for many services |
Typical use cases of Adaptive AUTOSAR
Adaptive AUTOSAR targets domains where flexibility compute and connectivity matter. Common examples include
• Automated driving stacks and domain controllers
• Vehicle central compute units that consolidate functions from many legacy ECUs
• Over the air update capable applications and third-party service hosting
• Complex human machine interface systems and data intensive telemetry
These examples reflect how the Adaptive Platform is used by OEMs and suppliers in modern vehicle architectures.
Release cadence and ecosystem
The AUTOSAR consortium maintains and evolves the Adaptive Platform through periodic releases. The standard documentation and explanatory papers are available from the AUTOSAR website. AUTOSAR is a large industry partnership with more than 350 partner organizations offering implementations tooling and ecosystem services. Core founding partners include BMW Robert Bosch Continental Mercedes Benz and Volkswagen among others.
The consortium structure and release history are documented on the AUTOSAR website. Each release typically introduces updated functional clusters improved API definitions and expanded support for emerging technologies such as automotive Ethernet and high-performance compute integration. For example, recent versions have added enhanced security service specifications and expanded execution management capabilities to better support over the air updates and mixed criticality workloads in modern vehicle architectures.
Development and tool-chain notes
Adaptive Applications are normally developed with modern C++ toolchains and tested against ARA stubs or platform implementations. The platform relies on a POSIX like environment so standard debuggers profilers and CI pipelines from mainstream software engineering apply. The AUTOSAR specifications define the API shapes and behavioral expectations while vendors provide full platform stacks tools and middleware to implement the standard. Major tool and software vendors offer Adaptive AUTOSAR solutions for integration and testing.
In practical workflows engineers often use virtualization to run multiple Adaptive AUTOSAR instances on a single workstation, enabling rapid service interaction testing before deployment on target ECUs. Additionally static analysis tools and compliance checkers are integrated into the CI pipeline to ensure that the developed applications conform to AUTOSAR API contracts and maintain interoperability across different supplier platforms.
Much like regulated online apotek platforms in Sweden, which help users safely navigate prescription medicines through strict compliance, verification and transparency, Automotive AUTOSAR provides a standardized and trusted framework for the automotive industry and help guiding manufacturers through complex software ecosystems, ensuring compliance with safety standards and enabling secure, informed, and reliable decisions in safety-critical vehicle systems.
Practical comparison of platform features
| Feature | Why it matters for a project | Adaptive AUTOSAR implication |
| Runtime update | Enables field fixes feature delivery and third-party apps | Supports runtime installation and controlled lifecycle |
| Service discovery | Supports modularity and multi supplier integration | Native service discovery is part of the platform |
| Middleware standardization | Reduces integration risk across suppliers | SOME IP and related specs provide a common service layer |
| High performance compute | Needed for sensor fusion machine learning and path planning | Platform is designed for HPC class ECUs running Linux style OS |
Final Thoughts
Adaptive AUTOSAR is a standards-based platform built to meet the needs of modern vehicle compute and software deployment scenarios. It complements Classic AUTOSAR by addressing flexibility high compute and service-oriented communication. Adoption is now broad across the automotive ecosystem and the standard continues to evolve via regular releases and a large industry partnership.
For engineering teams, the platform offers strong interoperability benefits along with new integration and security responsibilities that must be managed carefully. For example, the ability to deploy and update applications at runtime enables faster innovation cycles but requires robust execution management and security controls to prevent system instability or unauthorized access.
Additionally, as vehicles incorporate more complex sensor fusion and machine learning workloads Adaptive AUTOSAR’s modular architecture supports scaling compute resources while maintaining compliance with automotive safety and performance standards.
