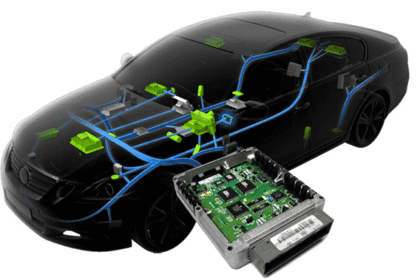
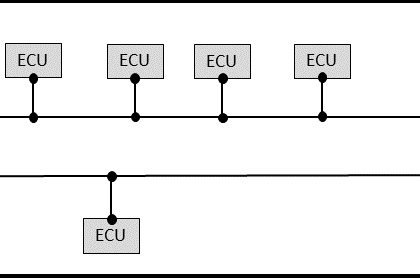
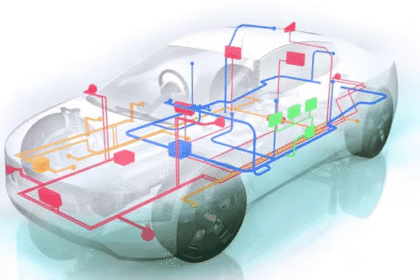
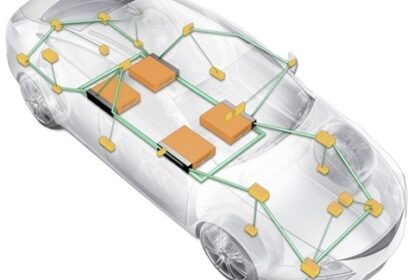
In modern vehicles and embedded systems, the CAN BUS and LIN protocol serve crucial but distinct roles. This article offers a deep technical comparison of CAN vs LIN, covering architecture, data rates...
CAN uses many ways to detect errors on the bus. There are majorly five error detection techniques in CAN bus protocol. These include Bit Monitoring, Bit Stuffing, Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC), Frame ...
The CAN Transport Protocol (CAN-TP) physical layer defines the hardware & electrical characteristics of the CAN protocol and specifies how data is transmitted over the physical medium. It includes...
A CAN controller manages communication over the CAN bus. It handles tasks such as message framing, error detection & message arbitration to ensure reliable data exchange between ECUs. CAN Controll...
Each CAN message in a CAN protocol has a unique hexadecimal Identifier called as CAN-ID or CAN Arbitration ID. A CAN-ID uniquely identifies a CAN message. Specifically, there are two types of frames o...
In the CAN protocol, USDT and UUDT diagnostic responses define a method for transmitting diagnostic data by dividing large amounts of information into smaller segments or frames. Understanding the dif...
What is Physical Addressing Vs Functional Addressing in CAN protocol? How do these two addressing schemes differ from each other? Physical addressing targets a specific ECU by using a unique address, ...
Reverse engineering a vehicle is a process of interpreting the meaning of message data without the aid of the database files or design documents. It involves a deep understanding of ECUs, in-vehicle n...