SAE J1939 communication is a in-vehicle networking protocol for ensuring seamless interaction between ECUs in heavy-duty vehicles. Understanding the different types of SAE J1939 communication is crucial for optimizing vehicle performance & diagnostics.
There are three types of communication in SAE J1939 protocol: Peer-to-peer, Broadcast and Proprietary. We will now discuss these in detail. These communication types determine how the network addresses, shares and interprets messages, influencing everything from fault detection to fuel efficiency.
A clear grasp of these types helps engineers implement robust communication strategies for complex vehicle systems.
Table of Contents
1. Destination specific (peer-to-peer) Communication
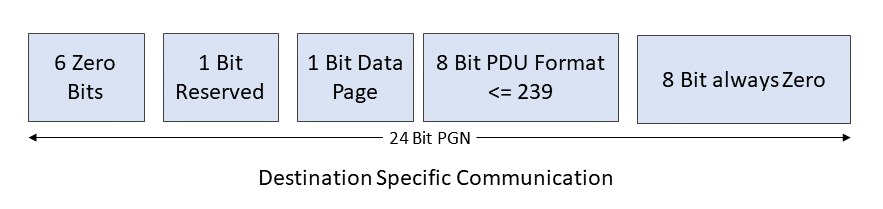
In this type of SAE J1939 communication., the system sends messages to a specific ECU using PDU1 (PDU Format values 0 to 239). The system requires a destination address.
2. Broadcast Communication
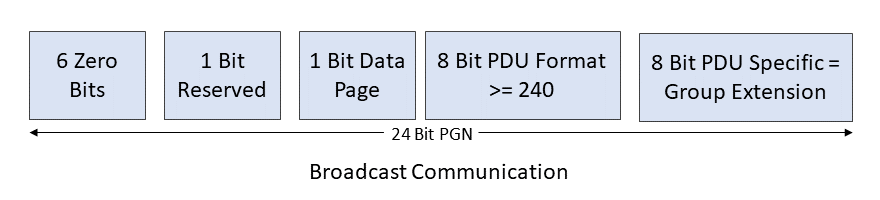
The system sends broadcast messages to all ECUs in the network when it needs to communicate with a larger audience. It uses PDU2 (PDU Format values 240 to 255).
NOTE: PDU Format is the most significant byte of the PGN. The least significant byte is considered to be zero.
For example, if the PDU Format equals 0xEA, then the PGN becomes 0xEA00 (59904 in decimal).
3. Proprietary Communication
Proprietary communication uses either PDU1 or PDU2 and transmits data as either destination-specific or broadcast. This type of communication uses proprietary PGNs.
NOTE: PGN = 18 bits + 6 zero bits= 24 bits (3 bytes) [Add 6 zero bits to the extreme left].
These are the three different types of message communication in SAE J1939 protocol.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the different types of SAE J1939 communication is essential for effective ECU coordination and reliable data exchange in heavy-duty vehicles.
Each communication type, namely peer-to-peer, broadcast and proprietary, serves specific use cases and, consequently, contributes to overall network efficiency.
By selecting the appropriate method, engineers can ensure optimized system performance and diagnostics. Mastery of these concepts is key to developing robust and scalable in-vehicle networks.




